AI in Cybersecurity: The Battle Between Algorithms and Hackers

Every 39 seconds, a cyberattack occurs somewhere in the world, and the shocking truth is that both attackers and defenders are using AI.
Seems like an opening line of a spy thriller, but this is real. From writing an email with auto-correction to creating an image for your office presentation using ChatGPT or navigating the shortest route under heavy traffic using a Car GPS, Artificial Intelligence is everywhere. So, AI in cybersecurity is no luxury as attacks are increasing, and AI can help effectively to prevent them, like a Protagonist.
Despite the debatable question- Is AI really helpful in the cybersecurity domain? The global AI in cybersecurity market is projected to show dynamic growth. According to the projections [Grandview Research], by 2030, it will be a $93.75 billion market with a CAGR of 24.4% (2025-2030).
AI’s subset technologies, such as natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML), will dominate, helping experts to magnify cybersecurity measures. From the region’s perspective, North America dominates the market with a 31.5% share to date.
You might have a question: What happens when AI becomes both the shield and the sword in cyberspace? Many readers have this same thought. Thus, considering its importance, we’ve created this article to help readers understand the significance of Artificial Intelligence in cybersecurity, including its role as a backbone to security, the basics, benefits, real-world applications, and more.
By the end of this blog, you’ll have valuable information that will help you adopt AI-powered security for sensitive business data and information.
Introduction: AI’s Role in Modern Cybersecurity
Artificial Intelligence has become one of the most powerful modern technologies in reality, influencing nearly every digital domain and industry. In cybersecurity, its role has emerged from a supportive analytical tool to a core defensive mechanism that continuously learns, adapts, and predicts threats.
As cyber threats become more complex and attacks are increasing every day, human-driven security measures alone can no longer handle all of these. Cybersecurity is no longer limited to firewalls, passwords, or antivirus programs; organizations must now know how to defend against sophisticated threats, e.g., ransomware, phishing, and zero-day exploits.
Therefore, how does AI act as a savior?
AI helps in a multitude of ways, such as providing automation and predictive capabilities that fortify both prevention and response in real-time. AI algorithms empower cybersecurity systems with the ability to analyze vast data, predict real-time threats, and automate responses to incidents, in which cybersecurity teams may fail using traditional methods.
A question arises- what cybersecurity threats can AI prevent?
Using AI, you can counter threats like phishing and email threats, malware and ransomware, insider threats, network intrusion, anomalous traffic, vulnerability exploits, credential theft, account compromise, and more.
From endpoint protection and network monitoring to phishing detection and identity management, AI-driven tools are becoming integral components of robust security strategies.
The things depend on how you utilize AI in cybersecurity. Let’s move back to the basics for a while before we proceed to read more.
What is AI in Cybersecurity?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a term that covers several smart technologies. The key ones you hear about are Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Artificial Neural Networks (ANN).
Combining AI and cybersecurity methods, let the machine simulate human-like analysis with high accuracy and faster than traditional methods.
Thus, in terms of talking about AI in cybersecurity, it involves the use of advanced algorithms, technologies like ML, ANN, and NLP, and AI-powered computational models to detect, identify, and mitigate cyber-risks effectively.
The key components of AI cybersecurity include:
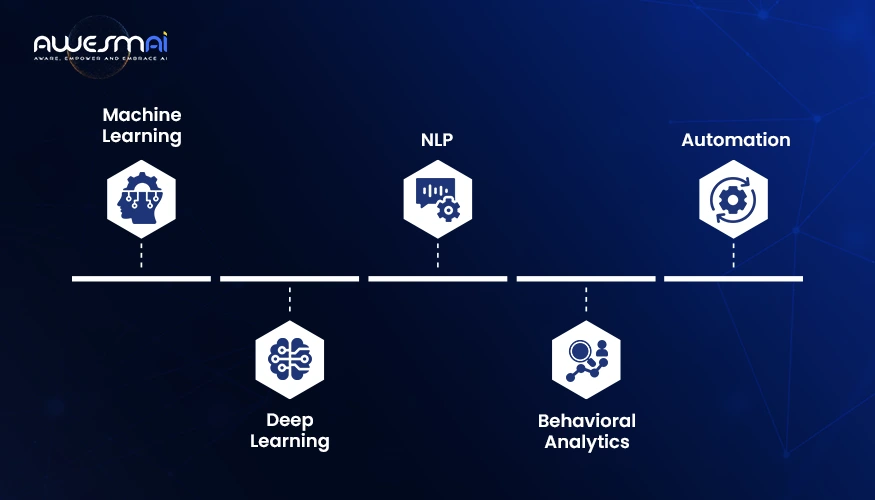
Machine Learning
Machine learning algorithms learn from the data and recognize patterns. In the context of cybersecurity, these programs analyze historical attack data, recognize attack patterns and anomalous traffic, and detect suspicious activity.
Deep Learning
DL is a subset of machine learning that mimics human brain processes. It helps security tools analyze complex data structures, such as network logs, images, or user behavior, through multilayer neural networks to identify hidden attack indicators.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP refers to the technology that helps AI to learn from human conversation using natural language. It helps in identifying phishing emails, social engineering attempts, and malicious content.
Behavioral Analytics
AI uses behavioral analytics to analyze user and system activity and set standards. If any suspicious activity occurs outside the set procedures and standards. In that case, it triggers alerts and detects insider threats or compromised accounts.
Automation
Here, automation stands for a procedure that is capable of responding to threats on its own. How does it work? It can isolate affected devices, block IP addresses, or update firewalls without human delay. You can also consider AI-powered agents as an example of cybersecurity automation using AI.
So, what are the key features and functions of AI in cybersecurity?
- Automated Threat Detection
- Rapid Incident Response
- Behavioral Analytics
- Vulnerability Management
Let’s move to the next section to understand more about the concept.
How AI is Enhancing Cyber Defense?

With the evolution of technology, cyberthreats are also growing in scale and becoming more complex every day, while traditional systems struggle to keep pace. Compared to conventional systems, AI for cybersecurity provides more effective ways to tackle and eliminate threats. That is why AI technology is reshaping the entire digital security landscape by adding layers of intelligence, automation, and adaptability that human experts or legacy tools can’t achieve.
Here it’s how:
Real-time Threat Detection
AI-driven systems use machine learning algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data, traffic, and user behavior, monitor networks, and endpoints. In contrast, the system creates a baseline for common activities and compares existing behavior with historical patterns to identify threats in real-time.
For example, AI-driven intrusion detection systems (IDS) can identify zero-day exploits by recognizing behavior without knowing the specific threat.
Automated Incident Response
Have you heard about SOAR? Its full form is Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response. So, AI empowers SOAR platforms to contain threats at any point of detection automatically. The mechanism automatically isolates infected devices, blocks malicious IP addresses, reduces human intervention, and saves time.
Suppose AI detects a compromised endpoint, the systems isolate the device from the network, revoke user credentials, and initiate analysis.
Reduction of False Positives
Manually filtering out false alarms is a challenge, but not when using AI in Cybersecurity. AI filters out false alarms and prioritizes actual threats. Therefore, professionals or teams can focus on true incidents and essential tasks instead of spending time handling false alerts.
Phishing and Malware Detection
Did you know that organizations using AI-driven email security are experiencing a 90% reduction in phishing attacks? Yes, that’s true. Natural Language Processing and Generative AI help in analyzing emails, websites, and messages to detect any phishing attacks. For example, detection of spoofed domains, deceptive wording, or fake login pages.
Enhanced Endpoint and Cloud Security
Mostly, organizations or large-scale enterprises use multiple cloud providers for infrastructure and apps. Due to the rising challenges of cyber threats, they need solutions that protect their infrastructure. From a security perspective, AI consistently collects and analyzes data across various cloud services and monitors devices and cloud environments to provide a comprehensive view of cloud risks and vulnerabilities. It helps cybersecurity professionals quickly address and eliminate threats.
AI vs. Hackers: A Constant Battle

So, what’s going on with AI in cybersecurity is that it is a double-edged sword: attackers are using it to enhance their attacks, while security teams are using it to prevent those attacks.
It is like – For every AI-powered firewall scanning for intrusions, a hacker is training a neural network to slip past it unnoticed. In this conflict, algorithms are battling with each other, one from the darker side and another from the positive side. Still, there is no winner as massive efforts are made from both sides.
How Hackers Are Using AI ?
Let’s understand how AI-powered cyberattacks happen!
- Automated Phishing: AI-generated emails or messages mimicking human tone, grammar, and personalization to deceive the targets with accuracy.
- Deepfake Scam: One of the biggest scams happening these days, where hackers are tracking people by blending realistic voice and videos to steal personal information or forcing them to transfer funds online.
- Evasive Malware: Hackers use AI-powered malware that is capable of rewriting its own code to evade traditional defence mechanisms, detection systems, and antivirus software.
- Automated Vulnerability Discovery: AI tools for hacking, help hackers to scan personal information, software, networks, and applications to detect security flaws for attacking.
- Data Harvesting: Machine learning models are used for analyzing stolen data to identify profitable targets, predict passwords based on behavioral analysis, and more.
- Social Engineering Bots: These are automated tools hackers use for carrying out social engineering attacks, mimicking real users in social platforms to steal and extract confidential details
Based on the above points, attackers are no longer just humans; they’re algorithms. Let’s explore the brighter side of AI in cybersecurity.
How it works – AI for Cybersecurity?
Cyber defense is not only limited to shielding, but it is also about hunting and eliminating threats strategically using AI. Thus, it’s like
- Adaptive Threat Detection: AI algorithms continuously learns from attack patterns and update themselves to recognize new threats
- Predictive Threat Intelligence: AI and machine learning powered algorithms analyze historical data, threat trends, and recognize patterns to predict attack scenarios and identify risk areas.
- Deception Technology: Cybersecurity professionals use AI to create fake systems or data that looks real but is not. Thus, when hacker attacks, the system records their move and helps teams to understand how hackers operate.
- AI-Driven Forensics: If any incident occurs, AI helps in analyzing digital footprints, tracing attack origins, strengthening weak points, and even hackers’ locations in extreme cases
- Vulnerability Management: For robust security, it is essential to maintain the IT ecosystem and infrastructure, especially if you are working at an enterprise-grade level. Here, AI and ML help in scanning the entire ecosystem for weaknesses and vulnerabilities.
Verdict
AI vs Hackers is a constant battle because both sides are evolving wth the technology. Each new security update leads to more improvised cyberattacks.
The concept in simple terms:
Defenders deploy AI → attackers adapt with AI countermeasures → defenders improve models → attackers innovate again.
Developing a smarter defense system is the best solution, but maintaining a higher ethical standard is more effective. AI in cybersecurity is a never-ending cycle, and the line between defense and offense is very thin; only high-grade preventive measures can help.
Key Benefits of AI in Cybersecurity
AI has gone beyond just a technical tool; it is now a strategic defensive mechanism for organizations to counter digital crimes against data security and privacy. Here are some potential benefits that AI in cybersecurity offers:
Speed and Real-time Response
As a surprising fact, AI-driven cybersecurity systems respond in milliseconds, whereas human teams take time to understand the threat and act accordingly.
Building Cyber Resilience
Instead of reactive defense, AI helps enterprises and organizations with proactive defense as it can predict risks, plan for incidents, and recover faster after attacks.
Scalable Approach
AI is not limited to a specific event; it can monitor millions of events across cloud and IT infrastructure without a lag. The AI-powered security systems can scale with the growing security requirements of an organization.
Improved Decision Making
Artificial Intelligence and machine learning in cybersecurity provide deeper insights, visualize risks, recommend preventive actions, and support compliance and governance. This allows security teams to make better decisions in real-time and even before an incident occurs.
Improved Productivity
AI reduces minor to significant chances of false positives/ alerts and prioritizes high-fidelity alerts so the security analysts can focus on strategic tasks with improved productivity.
Continuos Learning
The self-evolving capability of AI systems allows AI models for self-healing and improvement over time when processing new data, countering new threats, and accessing global threat intelligence.
Affordability
AI cybersecurity automates repetitive tasks such as log analysis, patching, and triage. As a result, it reduces the cost of handling security issues.
Challenges of Using AI in Cybersecurity
Now you have much information about how AI helps, but what is your view about whether it is easy to implement AI in cybersecurity? The truth is harsh, as there are challenges that need to be addressed when implementing a robust AI-driven security system to safeguard your enterprise’s data.
Let’s break down these challenges.
High Implementation Cost
Implementation of AI-driven cybersecurity systems requires advanced infrastructure, high computing models, and skilled professionals. Large-scale enterprises can afford it, but small-scale businesses struggle to adopt AI for cybersecurity, and the reason isthe expense of establishing infrastructure and hiring experts.
Solution: Use AIaaS, aka AI-as-a-service/ cloud-based security tools, start with a tailored project, train and upskill your workforce to manage security across systems.
Data Quality and Quantity
AI systems run on data, and you need vast, cleaned, and labelled data to train the models. If data is siloed, biased, and noised, it may create issues, and the results will be unexpected. Solution: Ensure cleaned datasets, regularly update datasets containing real-time threat information and intelligence, and establish a cross-review process to cross-check the output.
Over-Reliance and Automation Bias
Although automation is advantageous, overreliance is not ideal as it can create blind spots that your team may miss. Hackers can trick AI models through manipulated data and can exploit automated responses.
Solution: Put human experts in the loop, use multilayered defense strategies, and regularly test your systems for identifying vulnerabilities.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Integration with legacy systems is one of the challenges, as there may be compatibility issues or a version difference when integrating the latest AI models with old systems.
Solution: Use middleware, microservices, or APIs to integrate AI with legacy systems, and approach it in a planned, phased manner.
Privacy and Ethical Concerns
AI can process and analyze vast datasets for threat detection, but this can also raise ethical concerns such as privacy violations, data misuse, and surveillance.
Solution: Use a data minimization process(collect only useful data), encryption, and anonymization, and implement strict ethical standards for data use.
Real-World Applications of AI in Cybersecurity
AI in cybersecurity is not just a theory; it is more than a practical tool. According to IBM’s survey report, 67% of organizations worldwide are now using AI for threat detection and have adopted it as part of their security strategy.
From preventing phishing attacks to identifying hackers’ locations, AI is delivering a great impact across industries for cybersecurity. Here are some real-world applications of how AI is helping businesses with security practices.
E-mail Security
AI helps in email security effectively by analyzing signs of phishing. The best example is Google’s AI-powered Gmail filters, which block nearly 99.9% of spam, phishing emails, and emails containing malware before they reach the inbox, and that is approximately 10 million emails every minute.
Threat Detection and Prediction
IBM Watson is not a new name, and it has integrated AI into its platform to help cybersecurity teams. What sets it apart is understanding the context and intent behind the cyber threats using Natural Language processing, which helps analysts in reducing analysis time, correlating new threats with previous threat data.
Fraud Prevention
Most of the cyberthreats happen in the finance and banking industry, and the motive of hackers is to steal money digitally without leaving a clue. Considering the urgency, Payment technology company Visa invested $500 million in AI cybersecurity. The system utilizes machine learning for analyzing transactions in milliseconds and identifying any fraudulent activity. It provides outcomes based on the historical data, device, location, spending patterns, and past fraud trends.
Password Protection
One weak password is cracked, and everything is gone in an instant, including your privacy. Here, AI in cybersecurity offers robust security through authentication. Now most of the organizations are using AI tools such as CAPTCHA, AI-powered facial recognition, and biometric scanners to prevent threats and unauthentic login across their systems.
A prime example is Apple’s Face ID technology, which utilizes AI to authenticate the device owner and enable secure device unlocking and payments.
Network Defense
Darktrace’s Autonomous Response technology is one of the finest examples of AI in network defense. The technology identified and detected the attacker moving inside a hospital network during a ransomware attack and acted within 6 seconds.
AI helps in mapping normal traffic patterns and flagging unusual data flows, such as accessing sensitive information that has never been accessed before.
AI for IoT Threat Detection
IoT devices are vulnerable to cyberattacks as all devices connected within the same network; a single breach can expose the whole network if security is weak. Therefore, AI can help with anomaly detection.
The platforms like Vantage IQ engine and Microsoft Defender for IoT are some real-world example that helps in detecting anomalies in IoT environments, behavioral analytics, and more.
So, these are just a few examples and applications; the AI in the cybersecurity landscape is bigger than our thoughts. In the future, we’ll witness more advancements in this.
The Future of AI in Combating Cyber Threats
What’s next for AI in cybersecurity? It is a billion-dollar question now, as AI is evolving dynamically, and the future will be of AI-assisted cybersecurity systems. Here is what the future holds.
Autonomous Cyber Defense
In the near future, the AI systems will be autonomous in handling threats, detecting zero-day exploits, updating threat models, and more without human intervention. It also applies to automate the repetitive tasks within SOCs(Security Operations Centers), where the system will prioritize alerts based on rich context and respond to incidents in real-time.
Continuous Threat Hunting and Monitoring
With continuous evolution, AI will be stronger in detecting hidden threats and analyzing attack patterns. In simple words, it will go beyond reactive to predictive defense.
Generative AI for Threat Intelligence
Generative AI models will be capable of threat simulation and response training. It will help security teams to simulate realistic attack environments for better. Additionally, it will also help in generating synthetic datasets to train cybersecurity tools, while exposing only the information required for training.
Human AI Collaboration
AI will not replace human expertise; it will be a strategic ally to the experts, where AI cybersecurity systems will handle data monitoring, threat analysis, and automate repetitive tasks, and human experts will be more focused on strategic tasks to drive the best results.
Global AI Collaboration
Shared intelligence ecosystems are the next trend in which AI-powered cybersecurity systems will share intelligence across organizations and regions without exposing sensitive information to prevent and detect global threats.
AI-powered Deception
AI-driven deception technology will be capable of generating dynamic traps to trick the fraudsters and confuse them between genuine and fake targets.
Apart from these future trends, according to a genuine survey report, the artificial intelligence in the cybersecurity market size is set to be USD 146.52 billion by 2034, at a CAGR of 19.43%(2024-2030). This portrays a big picture of the future of AI in combating cyber threats. Still, there are some ethical considerations.
Ethical Considerations and Risks of AI in Cybersecurity
Till we reach this section, one thing is for sure: AI in cybersecurity brings myriads of benefits; however, it also has some ethical risks that a business or enterprise needs to understand before any implementation, such as:
Data Privacy
AI systems need large amounts of data to work. This often includes personal or sensitive business information. The problem starts when data is collected or used without full consent. If AI analyzes employee messages, customer data, or financial records, privacy can be at risk.
As a solution, companies must ensure that data is collected legally and transparently, inform users what data they are collecting, and how it will be used. Last but not least, only authoritative persons must have access to the sensitive data.
Bias in Decisions
AI only consumes data and learn from it, and if the data is biased, no one can stop AI from producing biased results. It may harm the sentiments of races, locals, regions, and nations. Thus, data must be monitored, cleaned, and unbiased before use.
Accountability
If something goes wrong when using AI for cybersecurity, who is responsible is a big question. There will be a blame game and no one will benefit from it, nor the company that has implemented for their client, nor the business that has invested. Companies should document who manages the system, who reviews its decisions, and who reports when something goes wrong.
Black-Box Problem
Sometimes AI works like a “black box.” It makes a decision, but people don’t understand why. In terms of security, this scenario can be dangerous and unavoidable. Suppose, if AI blocks or restricts a user or, in extreme cases, shuts down a system, the team must know the reason. Businesses should use Explainable AI tools that show how and why each decision is made. This helps build trust and accountability.
Dual-Use Dilemma
AI is a double-edged tool. While it helps protect businesses, hackers can also use it to plan stronger attacks. For example, AI makes it simple to create highly realistic fake voices, messages, or videos.
These are used to trick employees into giving up confidential information. It also lets hackers find weak spots in complex systems far faster than before. The companies must invest in AI tools that can detect fake content and AI-driven attacks, upskill their teams, and work with other organizations to share threat intelligence.
Conclusion: Striking a Balance in the AI-Cybersecurity Arms Race
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer merely a supporting function in cybersecurity; it has transitioned into a strategic ally essential for protecting businesses against the ever-evolving nature of digital threats. Still, with great power comes great responsibility. Companies must use AI carefully, keeping ethics, privacy, and accountability in mind. The future of AI-powered cybersecurity is bright, and we’ll witness the innovations. However, it will depend on how wisely businesses use AI’s capabilities and intelligence.
FAQ’s
How does AI work in cybersecurity?
AI in cybersecurity works like
- Collect and process large datasets.
- Identify and detect vulnerabilities.
- Analyze historical data and recognize attack patterns
- Adapt to the evolving threats and more.
Will AI ever take over human cybersecurity experts?
It’s just a myth, not a reality. In the future, AI will be a strategic partner to human experts to detect threats more effectively, automating repetitive tasks, enhancing productivity, and implementing advanced algorithms to counter the emerging threats.






