AI in Healthcare – How is Artificial Intelligence Being Used in Healthcare
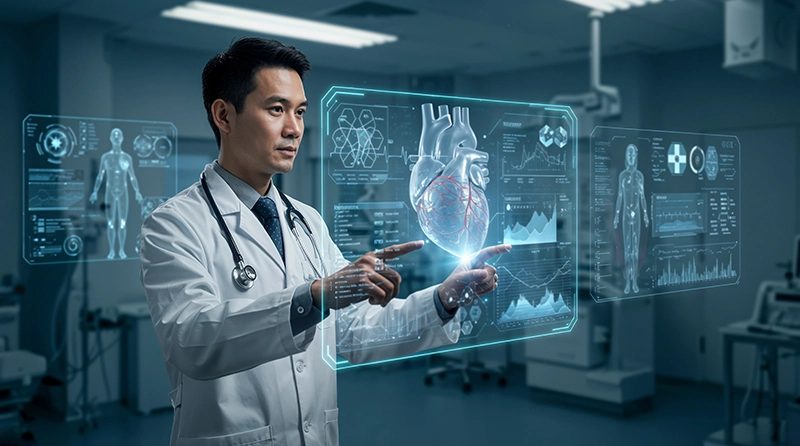

Imagine receiving a disease diagnosis before even showing any symptoms. Imagine doctors having an intelligent assistant that reviews thousands of medical images in just a few seconds to detect anomalies that the human eye may miss. This is not science fiction; this is part of the current reality involving AI in healthcare.
AI integrated into the healthcare industry is revolutionizing how practitioners diagnose, develop treatment plans, and ultimately improve outcomes for patients. Considering that healthcare organizations generate incredible amounts of patient data every day, AI applications in healthcare present unprecedented opportunities to make improvements in medical decision-making as well as the efficiency and personalization of care given.
A recent study reports that 83% of healthcare executives believe AI applications in healthcare will be a value that has not yet been considered in the next three years. While we pass through this technological transformation, knowledge of how artificial intelligence in healthcare functions and affects is vital for patients and providers alike.
What is AI in healthcare?
Artificial intelligence in healthcare refers specifically to the algorithms and software that act as a substitute for human reasoning when it comes to analyzing complex medical data. While previously, healthcare technology has been rule-based and pre-defined, AI in healthcare focuses on learning from data patterns and building its effectiveness over time, regardless of any particular programming.
Key Components of AI in Healthcare
- Machine learning: Algorithms that improve themselves based on experience, which means that the systems are capable of discovering patterns in the patient data, predicting outcomes, and recommending/offering tailored treatment plans.
- Deep learning: A subfield of machine learning that uses neural networks with multiple layers to simultaneously take into account many different attributes; particularly useful for analyzing medical images and discovering subtle abnormalities.
- Natural language processing: Among other things, Natural Language Processing (NLP) is the technology used by computers in an attempt to decipher text and speech and generate those languages. This also finds its utility in the analysis of clinical notes, medical literature, as well as patient communications.
The one core difference between AI in healthcare and traditional healthcare technology is flexibility. Traditional systems are set up to carry out only specific, rule-based tasks; AI systems continuously learn from new data and thus improve their accuracy and effectiveness over time. While electronic health records systems simply help collect information, healthcare AI can interpret that information to predict disease progression, recommend possible treatments, and identify at-risk patients.
AI in healthcare statistics
The healthcare sector experienced rapid growth of artificial intelligence (AI) applications throughout 2025 through multiple important developments across various healthcare fields. The following statistics show the present state of healthcare, together with AI’s influence on medical practice.
- The AI in healthcare market will expand to $187.7 billion by 2030 with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 38.62% between 2024 and 2030.
- One of the AI applications in healthcare is visible in radiology. Radiology benefits from AI tools that detect brain tumors, strokes, and breast cancer. The FDA recently approved over 340 AI that play a vital role in urgent case screening to boost diagnosis speed and accuracy.
- AI in the healthcare industry decreases expenses through better diagnostic precision and enhanced operational performance. AI solutions achieve an 85% improvement in diagnostic accuracy and a 40% boost in operational efficiency, which leads to substantial cost reductions.
- The Harvard Medical School developed an AI model named CHIEF, which represents a groundbreaking achievement. CHIEF represents the Clinical Histopathology Imaging Evaluation Foundation. The model achieved 94% precision in cancer detection across 15 datasets containing information about 11 different cancer types.
- The Snowflake survey demonstrates that 92% of healthcare organizations using AI report positive returns from their investments, while 98% intend to boost their AI spending in 2025.
Benefits of AI in healthcare
Artificial intelligence in the healthcare sector delivers huge advantages for healthcare providers, patients, and the entire medical ecosystem. Below are some of the ways they can be achieved.
Enhanced Diagnosis and Treatment
Artificial intelligence significantly impacts one of the critical sectors of healthcare, which is accuracy in diagnosis and treatment planning. For instance, machine learning algorithms process vast amounts of medical data to identify patterns and relationships that perhaps only human intervention could highlight. AI systems analyze medical images to detect small anomalies that might indicate diseases like cancer at an earlier and thus more treatable stage.
Streamlined Administrative Processes
Physicians and nurses dedicate a lot of time to fighting tedious administrative tasks. AI in healthcare examples include automation systems designed to take over the scheduling of appointments, insurance verification, and billing, thereby freeing up clinical staff to spend more time caring for patients instead of paperwork.
Personalized Medicine
Among the most common AI applications in healthcare, rapidly gaining traction today is the ability to develop personal treatment plans. This feat is accomplished by AI algorithms that are powered to ‘read’ the patient data, including genomics, medical history, and lifestyle, and then move towards a ‘one-on-one’ approach based on specific patient characteristics.
Improved Patient Engagement
Health AIs within the industrial sector enhance customer interaction through digital health assistants and telemonitoring systems. These technologies provide personalized health information to the patients, remind them about their medication regimens, and continuously monitor their vital signs; hence, they can play an active role in controlling their health.
Research and Drug Discovery
AI uses in healthcare are not just accelerated drug discovery and development. For instance, when AI algorithms interpret biological data to identify diseases, it enables predictions about the interactions of compounds with biological targets and optimally designs trials, potentially reducing both time and cost in bringing new therapies into the marketplace.
Pro Tip: A healthcare organization should start its AI initiative with narrowly defined use cases that address specific pain points, instead of an over-the-top, blanket deployment of AI across its operational components.
Pros and cons of AI in healthcare
While AI in healthcare holds tremendous promise, it’s important to examine both the benefits and the challenges that are being encountered.
Pros:
- Increased accuracy: Machine Learning algorithms are capable of analyzing and interpreting vast amounts of data much more effectively than humans, thus reducing the chances of diagnostic mistakes.
- Efficiency improvements: A lot of day-to-day jobs are being automated so that healthcare providers can fully focus on the patient’s needs.
- Continuous learning: The more data AI algorithms gather, the smarter and more accurate they become over time.
- 24/7 availability: AI in healthcare systems can work 24/7 or provide constant monitoring and support, unlike humans.
- Reduced cost: The ultimate delivery cost of healthcare will be reduced because AI in the healthcare industry is increasing efficiency, decreasing readmissions, and enabling early interventions.
Cons:
- Cost of implementation: At the beginning of implementation, it may be costly to apply AI technology in healthcare, which includes costs as a result of hardware acquisition, software development or procurement, and staff training.
- Data privacy issues: Significant concerns of privacy and security are related to the usage of sensitive patient data.
- Integration challenges: Deployment of AI applications in healthcare usually implies their interfacing with the existing systems, which are often quite intricate.
- Potential for bias: One concern is that AI algorithms may inherit the biases existing in the training data and thus provide different care.
- Regulatory uncertainties: The pace of AI development in healthcare is too rapid for regulators to keep up with.
| Aspect | Pros | Cons |
| Diagnosis | High accuracy and speed increase a routine accuracy potential | Algorithmic bias may arise in diagnosis. |
| Patient Care | Personalized treatment plans may be a great asset | Might reduce the human touch in healthcare. |
| Efficiency | Can be improved by the automation of routine tasks | Might have substantial implementation costs |
| Accessibility | Available 24/7 to everyone | May create a digital divide for some populations |
| Data Management | Better utilization of health data may happen | Privacy and security concerns will rise. |
Use Cases & Applications of AI in Healthcare
The healthcare continuum from prevention through diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing care involves practical applications of AI in healthcare.
Medical Imaging and Diagnostics
AI in medical data is among the best examples of AI in healthcare that uses advanced algorithms to analyze medical pictures, including X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, for detecting abnormalities with high accuracy. Deep learning algorithms can learn to find patterns and anomalies which others may not detect, thus improving the early diagnosis of cancer, cardiovascular diseases as well as neurologic disorders.
Predictive Analytics and Risk Assessment
AI in the medicine and healthcare sectors does better in the use of patient data for diagnosis and prognosis of health risks or diseases. These systems are able to tell who will develop certain diseases or have complications in the future, therefore pre-conditions can be managed.
Virtual Health Assistants and Chatbots
AI agents in the healthcare sector respond quickly to common health inquiries, give medication reminders, and help manage symptoms through guidance. These instruments improve patient participation at the same time, lightening the work of the health care provider from constant questioning.
Precision Medicine and Treatment Planning
AI healthcare applications support the tenet of precision medicine by evaluating genetic data, biomarkers, and patient history to propose tailored treatment schedules. Therefore, this would enhance the efficacy of the treatment while reducing adverse effects.
Drug Discovery and Development
Examples of AI applications in healthcare include accelerating drug research through the analysis of biological data, predictions of molecular interactions, and identification of potential drug candidates. AI algorithms can screen compounds much more effectively than the conventional approach, which might reduce the time as well as the cost involved in developing drugs.
Robotic Surgery
Surgical robots enhance the ability of surgeons to perform with greater precision and control. Such systems scrutinize pre-operative medical images and data, thereby planning and conducting surgeries in a minimally invasive manner.
Administrative Workflow Optimization
AI in the healthcare sector achieves efficiencies in operational processes, for example, appointment scheduling, billing, coding, and others. NLP can automatically create clinical documentation from physician-patient dialogs which will decrease the administrative burden.
Remote Patient Monitoring
Artificial Intelligence in healthcare allows for the constant surveillance of patients through wearable devices and sensors. These systems monitor real-time health data to find any alarming alteration and notify healthcare professionals when intervention is required.
Pro tip: Healthcare organizations applying AI should enhance human expertise rather than replace it. Hence, create collaborative workflows in which AI takes care of the mundane so clinicians can concentrate on complex decision-making and relationships with their patients.
Generative AI in Healthcare [New Frontier]
Generative AI in healthcare is the cutting edge of advanced artificial intelligence in the healthcare sector, producing new content, designs, and solutions instead of just generating responses from existing material.
Advanced Medical Imaging Generation
Generative AI in healthcare can create synthetic medical images for diagnostic algorithms. Such datasets are extremely valuable, though often rare, for training models, especially for rare conditions.
Drug Design and Discovery
Generative models speed up the search for new pharmacological drugs by offering possible molecular structures that might exhibit the desired therapeutic properties. Such systems in silico generate and evaluate millions of potential molecules at the outset, greatly increasing efficiency while reducing the time and cost related to initial drug discovery.
Synthetic Patient Data Creation
One of the most interesting applications of generative AI within the healthcare sector is in creating synthetic patient datasets. These datasets are statistically representative of actual patient data, yet devoid of any individual’s personal information. Such synthetic data permits a much stronger degree of training for algorithms and research, all in compliance with data privacy regulations.
Medical Education and Simulation
Generative models thus are important in helping medical students acquire realistic simulations where practitioners can experiment with a wide range of techniques and decisions in an artificial environment before actually going out into the real world with live patients. Furthermore, these simulations could be designed for rare conditions or complications that the trainee would otherwise be unlikely to encounter during their education.
Personalized Treatment Planning
AI can develop personalized treatment plans by predicting the impact of several interventions on a particular intervention that is most tailored to the unique characteristics of that patient. This will further enhance the strategies of precision medicine by tailoring treatments even more exquisitely to individuals.
Generative models mark a significant evolution within AI in the healthcare industry: from an interrogative passive model to an informative assistant, and finally to a co-creator in medical innovation and patient care. The deeper these technologies go, the more inexplicable their role in healthcare delivery will be.
Companies Using AI in Healthcare
Countless of those connected to the healthcare sector are at the forefront of using AI, and are creating intelligent answers for many issues that affect all segments of the healthcare area:
Google Health
Google Health has developed AI models for medical imaging that are capable of detecting diabetic retinopathy and breast cancer at a level comparable to that of human experts. Their systems scrutinize retinal images and mammograms to spot abnormalities earlier than in conventional screening processes.
IBM Watson Health
IBM’s Watson uses AI in the medicine and healthcare sectors through natural language processing combined with machine learning to survey tons of medical literature as well as patient information. Watson helps providers make evidence-based decisions and find treatment options for even the most complex conditions.
Microsoft Healthcare
Microsoft uses its cloud and AI capabilities to develop healthcare solutions, particularly in precision medicine and healthcare analytics. One of these is Azure Health Bot, which applies AI in healthcare to develop conversational interfaces for engaging patients and triaging them.
Tempus
Tempus uses AI in the healthcare industry to combine clinical and molecular data for tailored cancer treatment. On its platform, oncologists are able to make treatment decisions based on data gathered from a patient’s genetic profile and similar cases.
Babylon Health
Babylon uses AI applications in the healthcare sector to offer virtual consultations and symptom checking. Their AI-powered triage tool helps patients figure out what level of care is needed based on their symptoms.
PathAI
PathAI develops machine-learning technologies that enable pathologists to diagnose more accurately. The platform enhances the accuracy of diagnoses and helps identify patients who may be appropriate for certain therapies or clinical trials.
Atomwise
Atomwise uses artificial intelligence in healthcare to revolutionize the discovery of drugs. Deep learning algorithms predict which molecules will bind well with target proteins. This has led to the identification of promising candidates for conditions ranging from Ebola to multiple sclerosis.
Butterfly Network
Butterfly Network developed an ultrasound device, portable and enhanced with AI, to make medical imaging access easier. The technology is a combination of hardware and software, healthcare AI-optimized to direct the user and interpret the ultrasound images.
These companies are just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to forward-thinking businesses that use AI in healthcare with the sole aim of better patient outcomes, increased efficiency, and pushing further medical discovery.
Challenges and Considerations of Using AI in Healthcare
Even though AI can completely change the system, its implementation in the healthcare sector is faced with many crucial problems that must be solved:
Data Quality and Integration
AI in the healthcare industry uses data that is high-quality, structured, and organized. However, healthcare data is often disconnected living in siloed systems with different formats and standards. Yet this continues to be a big problem; how to ensure the integrity of data, its compatibility as well and accessibility on different platforms from different vendors.
Privacy and Security Concerns
The sensitive nature of health information requires strong privacy protections. AI applications in healthcare must operate under the same regulations, like HIPAA, while accessing enough data to be effective. This is an eternal challenge: balancing innovation with patient privacy.
Regulatory Approval Processes
The regulatory landscape for AI in healthcare is continually evolving. Approval for medical devices and software that incorporate AI requires navigating through convoluted regulatory frameworks not inherently designed with adaptive, learning algorithms in mind.
Algorithmic Bias and Fairness
AI systems could inadvertently reinforce or even magnify existing healthcare disparities due to biased training data. Equitable delivery of care by AI in medicine and healthcare among various demographic groups will require intentionally designed algorithms and continuous monitoring.
Clinical Validation and Trust
Healthcare professionals will likely be reluctant to use any AI in the healthcare system whenever there is no strong evidence showing that these AIs are safe and effective. Trust can be formulated with the help of transparent development processes, and validation studies that are comprehensive and effective communication regarding what an AI system can and cannot do.
Implementation and Workflow Integration
An AI in healthcare example of successful AI integration into clinical workflows requires careful planning of implementation. Solutions that disrupt normal processes or add complexity will likely be met with resistance, regardless of technical merit.
Ethical Considerations
The application of AI in healthcare presents many ethical issues, such as who is to make decisions, who is accountable for a mistake, and where the line should be drawn regarding automation in sensitive healthcare environments.
Pro tip: Healthcare organizations using AI should set up multidisciplinary governance committees that include clinical, technical, ethical, and patient representatives to oversee the responsible deployment of AI.
What is the cost of implementing AI in healthcare?
An understanding of the monetary impact of adopting AI in healthcare enables organizations to make effective plans for this technological changeover.
Initial Investment
The implementation of AI in the healthcare industry requires an upfront investment of capital:
- Software Licensing: Enterprise software licensing for AI in healthcare solutions can cost between $100,000 and $500,000 per year for medium-sized healthcare organizations.
- Hardware Infrastructure: Hardware costs can range anywhere between $50,000 and several million, depending on whether the solution is cloud-based or on-premise.
- Integration Services: Connecting AI applications in healthcare to existing systems often costs between $50,000 and $200,000 per integration project.
- Staff Training: Training healthcare workers to use AI systems effectively typically costs between $1,000 and $5,000 per person.
Ongoing Expenses
Beyond initial implementation, AI in healthcare involves continuous costs:
- Updates and Maintenance: The annual maintenance fee is usually in the range of 15-20% of the initial cost of a license.
- Technical Support: Specialized support services may cost you $50,000-$150,000 annually.
- Data Storage and Processing: The costs for cloud computing and data management range from $10,000 to over $100,000 a month, depending on the amount of data.
- Compliance and Security: Adding systems to ensure that regulatory requirements are met costs an additional $50,000-$200,000 yearly.
Return on Investment
Despite the upfront costs, AI in healthcare offers a significant return on investment through:
- Efficiency Gains: Eliminating administrative burdens costs $15-$30 per patient encounter.
- Reduction of Errors: AI-enabled diagnosis and treatment planning can reduce expensive medical errors by as much as 30-50%.
- Improved Resource Allocation: Facilities can be stretched by another 15%-25% under optimal patient flow and resource management, without any physical expansion.
- Preventive Care Enhancement: AI uses in healthcare can reduce inpatient costs by approximately 20-30% through early interventions among at-risk patients.
Organizations implementing AI in healthcare tend to break even on their investments within 18 to 36 months. However, some organizations experience Positive ROI within a mere 12-month period when targeted applications are used.
| Implementation Phase | Cost Range | Primary Factors |
| Initial Setup | $150,000–$1M+ | Organization size, AI complexity |
| Annual Operation | $100,000–$500,000 | Data volume, system scope |
| Staff Training | $50,000–$200,000 | Number of users, solution complexity |
| ROI Timeline | 12–36 months | Use case specificity, implementation quality |
What is the future of AI in healthcare
Applications of artificial intelligence in healthcare are integrated, increasingly sophisticated, and personalized, thereby changing the way healthcare is delivered much more fundamentally.
AI Trends in Healthcare
Within healthcare, AI is driving the emergence of several critical trends that will shape the medicine of tomorrow.
- Multimodal AI: Future systems will analyze genomic data, medical images, clinical notes, and real-time monitoring data simultaneously to obtain a holistic view of the patient.
- Federated Learning: It enables AI in healthcare models to glean insights from data available across multiple institutions, thereby accelerating development while keeping patient information confidential.
- AI and Human Collaboration: The future of AI in the healthcare industry is as an adjunct to the clinician, rather than a replacement, handling routine tasks while humans focus on higher-order decision-making and relationships with their patients.
- Ambient Clinical Intelligence: AI will seamlessly observe the clinical interaction, generate the paperwork automatically, and capture pertinent information right at the point of care.
- Decentralized Healthcare Delivery: Innovations in artificial intelligence for Healthcare will enable more effective remote monitoring and telehealth services, thereby shifting healthcare even further from hospitals into homes and community settings.
Emerging Applications
In the near future, there will be several potential emerging examples of AI in healthcare that we have observed.
- Digital Twins: These customized computational models, which represent the physiology of a particular patient, would allow physicians to experiment with virtual treatments before actually administering them to the patient.
- Neural Interfaces: Brain-to-computer direct interfaces, which are improved by AI in medical and healthcare applications will completely change the treatment of neurological disorders and open new assistive technologies for disabled people.
- Automated Drug Compounding: Such robotic systems, driven by artificial intelligence, will compound drugs for patients with unprecedented accuracy.
- Predictive Population Health Management: Sophisticated analytics will identify new health trends in populations before they appear in routine surveillance, thereby permitting proactive public health interventions.
Pro tip: Healthcare organizations should come up with longer-term AI strategies that are flexible and scalable because the most interesting applications might emerge pretty quickly as technology development progresses.
Conclusion
The integration of artificial intelligence in healthcare is one of the most significant milestones ever recorded in medical practice. The healthcare sector is experiencing a profound revolution within the care delivery models and management frameworks due to AI technologies that enhance diagnostic precision and treatment customization, and simultaneously introduce efficacy in administrative functions.
AI applications in the healthcare ecosystem address the diverse needs of various stakeholders in the healthcare industry, including patients, providers, researchers, and healthcare organizations. Healthcare is hence impacted by artificial intelligence in terms of not only patient outcomes but also operational efficiency and effectiveness measures.
There are several important challenges associated with the implementation of AI in healthcare that need to be addressed so that the full potential of AI applications in healthcare can be liberated from its current shackles, including data quality issues, privacy concerns, integration issues, regulatory requirements, and ethical considerations. Furthermore, the gradual application of AI by health organizations will require technical as well as human factors.
Mark the impact that future AI development in healthcare will be more revolutionary, as innovations and new applications are continually being developed. Healthcare organizations that thrive in such a constantly changing environment would depend on AI to empower healthcare providers while keeping human expertise and compassion.
The use of smart AI in medicine and healthcare is paving a path for the future of healthcare which will have the potential to offer to every individual patient a high-level, specific, personalized, convenient, and effective medical help.
FAQs
How is AI used in healthcare?
AI in healthcare exists in several domains, such as medical imaging interpretation, predictive analytics regarding disease risk, virtual health assistants, precision medicine, drug discovery, robotic surgery, administrative workflow optimization, and remote patient monitoring. All these AI applications in healthcare aim to boost diagnostic accuracy, improve treatment planning efficiency, streamline healthcare operations, and provide patients with more tailored care.
How is AI used in hospitals?
AI in the healthcare industry supports clinical decision-making through diagnostic tools and treatment recommendations; aids in determining optimal patient flow and resource allocation; automates administrative tasks like scheduling and documentation; enhances precision in surgery through AI-guided robotics; and manages medication. All these examples of AI in healthcare enable hospitals to be more efficient, make fewer mistakes, and improve patient outcomes while keeping costs in line.
Can AI replace doctors?
No, artificial intelligence in healthcare cannot replace doctors. While AI is very good at recognizing patterns and processing huge amounts of data, it does not have the clinical judgment, ethical reasoning, empathy, and context understanding that a doctor provides.
Hence, AI in medicine and healthcare works best as a collaborative tool that enhances what an already trained physician can do, taking care of the mundane while offering support in decisions when physicians concentrate on complex clinical reasoning and meaningful interactions with patients.
What is the role of AI in medical imaging?
AI in healthcare has been a revolutionary aspect of medical imaging by interpreting images such as X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and ultrasounds to find anomalies with great accuracy. Such minute patterns that go unnoticed by humans are picked up by deep learning algorithms, thereby facilitating the early detection of cancers, cardiovascular diseases, and neurological disorders. AI applications in healthcare imaging also streamline workflows by flagging urgent cases and reducing radiologist fatigue.
Is AI used in mental health care?
Yes, AI in healthcare is being widely applied to support structures for mental health services through, among others, chatbots that deliver cognitive behavioral therapy, systems analyzing speech patterns to diagnose conditions like depression or anxiety, predictive models identifying patients at risk of a crisis, and digital phenotyping tools monitoring changes in behavior through smartphone usage.
All these illustrations of AI use cases in the healthcare sector provide greater accessibility to mental health support; they facilitate earlier intervention and help in the personalization of treatment approaches.
Which AI tools are used by pharma companies?
Pharmaceutical companies use various AI in healthcare solutions such as molecule design platforms that synthesize new drug candidates, predictive models that emulate the interaction of compounds with biological targets, algorithms that determine the best patient populations for clinical trials, systems that analyze real-world evidence to identify safety signals and new indications for already approved drugs, and supply chain optimization tools. All these AI applications in healthcare speed up the drug discovery process, lower development costs, and increase success rates in the pharmaceutical value chain.