What is Artificial Intelligence? Definition, Types, Use Cases, Benefits

Do you remember the movie I-Robot? It was a science fiction movie, and people watched it with deeper interest. However, as Artificial Intelligence progresses at a rapid pace, it will become a reality very soon. Imagine a robotic house helper that doesn’t require instructions, or a robotic version of Siri or Alexa sitting beside you at your office desk.
Another real-world example is the Sophia Robot. The fun fact is that she even has her own Instagram account—“@realsophiarobot.” Although Hanson Robotics manages this account, she may post on her own one day. From house help to a social media-savvy robot, AI is steadily moving from fiction to reality. The AI market is expected to reach $1.01 trillion by 2031, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 26.60%(2025-2031).
More than mimicking human intelligence, AI enables devices to identify objects, understand human language using NLP (natural language processing), automate tasks through machine learning (ML), and perform other functions, such as those in autonomous vehicles.
It all started in 1950 when AI was introduced to this world, and by the end of 2025, something will be more exciting than we think. It is available in various types with multiple benefits and real-world use cases.
Considering all points and inspired by the evolution of AI, we have created a detailed guide that will walk you through various aspects, from a simple definition to how you can use it ethically for personal or professional purposes.
So, fasten up your seatbelts. Here we go!
Let’s have a look at the stats first.
Top AI Market Key Stats
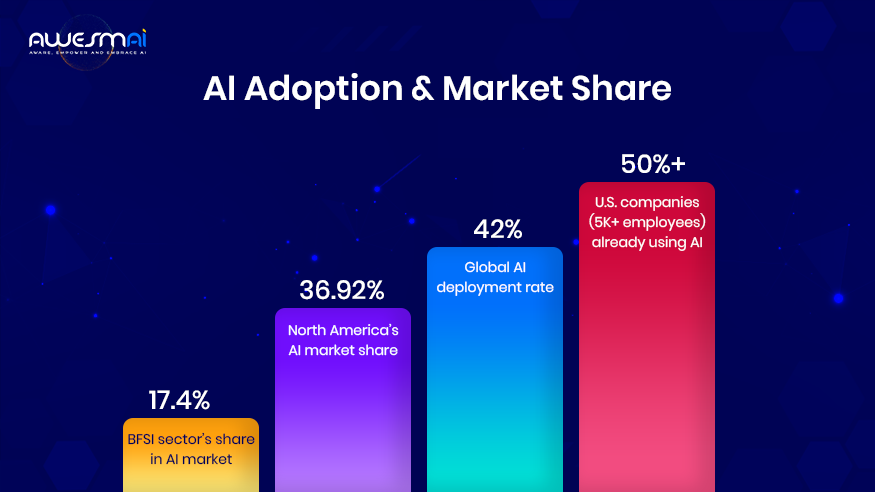
- The global AI deployment rate is 42%, and over 50% of US companies with more than 5K employees use AI.
- Compared to the global region, North America holds a dominant position with a 36.92% market share and is projected to reach $299.64 billion by 2026.
- The current size of the AI market in the APAC (Asia Pacific) region is US$85.15 billion (2025).
- Along with other regions, the MENA (Middle East and North Africa) is also progressing in AI adoption. At a CAGR of 26.23, the market volume is poised to reach USD 37.81 billion by 2031.
- Experts predict that by the end of 2025, 97 million people will be employed in the AI space.
- To date, the BFSI sector is one of the most significant users of AI, with a 17.4% market share.
- Although maximum revenue is generated through Deep Learning, Machine Learning, NLP, and Machine Vision, Context-aware AI is the fastest-growing segment (2024-2030).
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a combination of technologies that mimic or simulate human intelligence and enable computers or machines to perform tasks that require human intelligence. These tasks can include learning, problem-solving, decision-making, speech recognition, image recognition, and object identification through vision.
In other words, AI systems are adaptable to situations, can process large data sets, extract information from text, and perform almost all tasks that humans do commonly. In some cases, they require human supervision, but now researchers are more interested in Agentic AI that handles all tasks autonomously.
The secret about AI is that it is an umbrella term comprising multiple technologies. The key technologies are Machine Learning, Artificial Neural Networks, Natural Language Processing, and Deep Learning.
It is interesting that there are some disagreements about Artificial Intelligence, but it has proved that it can do the tasks that humans do, such as data analysis, content creation, driving a car using computer vision, and even solving a puzzle like the “Cap Set Puzzle.”
So, before you ask someone, Can AI solve riddles? Be careful!
Some readers might want to know how AI has come a long way.
So, it is such an interesting thing to explore the history of AI. Are you ready?
Let’s continue with the blog!
What Is the History of Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
The core idea that gave birth to AI is “A machine that thinks,” and its credit goes to the father of computer science and a great mathematician, Alan Turing. However, research laid down the foundation for AI in the early 1900s.
In 1921, the term “Robot” was coined during a science fiction play named “Rossum’s Universal Robots.” In 1929, Professor Makoto Nishimura introduced the first Japanese robot named Gakutensoku, and in 1949, Edmund Callis Berkley published a book comparing computer models to the human brain. However, the actual birth of AI is considered to be 1950-1956.
Let’s explore what is hidden in the history of AI!
1. Early Conceptualization (1950-1956)
The interest in AI surged in the 1950s with Alan Turing’s publication of “Computer Machinery and Intelligence,”-which later became the Turing Test. The term “artificial intelligence”-was coined and gained popularity. Arthur Samuel independently learned checkers in 1952, and John McCarthy’s 1955 workshop on AI marked its first use.
2. AI Got Its Name (1956)
When did AI get its name? It is one of the most interesting questions usually asked by beginners while researching. In 1955, John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Nathaniel Rochester, and Claude Shannon proposed the Dartmouth Summer Research Project on Artificial Intelligence, a workshop held in 1956. That’s when the term “Artificial Intelligence” came into existence.
Later, in 1956, Allen Newell and Herbert Simon developed the Logic Theorist, the first AI program to prove mathematical theorems.
3. Rise of AI (1960-1970s)
From the early 1960s to the 1980s, artificial intelligence (AI) experienced growth and challenges, but it became a popular topic among researchers. This was the time when AI got its first spark.
For example, John McCarthy introduced the programming language LISP in 1958, Arthur Samuel introduced “Machine Learning” in 1959, and General Motors introduced the Unimate robot in 1961.
It progressed over the years, and in 1979, AAAI, aka the American Association of Artificial Intelligence, was formed(alias the Association for the Advancement of AI).
4. The AI Boom (1980-1987)
In the early 1980s, AI boomed, and the reasons were significant breakthroughs in research and government initiatives in terms of funding. For example, at the First AAAI conference at Stanford in 1980, the Japanese government allocated $855 as research funding in 1981. However, the AAAI warned of an “AI Winter” in 1984, and the first autonomous drawing program, AARON, was showcased in 1985.
Deep Learning and Expert Systems gained traction, enabling computers to learn from mistakes and make decisions.
5. AI Winter (1987-1993)
As AAI cautioned, an AI Winter took place due to low interest in AI, reduced research funding, and few breakthroughs. Setbacks like the cancellation of the Fifth Generation program, strategic computing projects, and the slow adoption of expert systems induced this. The key dates are 1987’s collapse in the market for niche LISP-specific hardware and 1988’s invention of Jabberwocky.
6. An Era of AI Agents(1993-2011)
In the early 1990s, AI got its second boom in terms of AI research and the introduction of AI systems. One of the most interesting examples is “Deep Blue,” developed by IBM(1997). The fun fact is that it won a match with world chess champion Garry Kasparov and became the first AI program to beat human intelligence.
Later, there were more notable events, such as Windows’s release of speech recognition software in 1997, Kismet(a robot that simulated human emotions in 2000), Roomba(a robotic vacuum cleaner), the Mars landings(2003, rover bots), AI integration in advertising(Netflix, Twitter, and Facebook), Xbox 360 Kinect(Microsoft), Watson winning Jeopardy(IBM) in 2011, and Apple’s Siri.
7. AGI aka. Artificial General Intelligence (2012- Till Date)
Now, AI is everywhere, in everything from content creation to video editing, from making a crucial business decision to demand forecasting for production. Whatever use cases we are witnessing are the result of advancements in AI since 2012.
During these years, multiple key events occurred in the history of AI, but 2020 was notable when Open AI introduced GPT-3, which can write code, song lyrics, an article, a sales tagline, and more that require human expertise. In 2021, another milestone was Dall-E, an AI that can understand and describe images.
So, from 2022 to this year, key events are:
- 2022: launch of ChatGPT(AI Chatbot), MidJourney(AI image generation), Stable Diffusion(another popular AI image generation tool).
- 2023: Meta’s Large Language Model LLaMA for research, AI integration in Bing search engine, Open AI’s GPT-4, Google’s conversation AI- Bard.
- 2024: AI saw wider adoption worldwide, and the European Union passed the AI Act to regulate AI technologies
Highlights for 2025
- Increased AI Adoption in the Workplace
- More GenAI App Integration
- AI-Powered Customer Experiences
- Enhanced AI Reasoning
- Agentic AI Development
There are myriad use cases and adoptions across industries, such as AI in healthcare, AI in the food industry, AI in logistics, AI in supply chain, etc.
Now, here, a question arises – what comes next?
There is no doubt that AI is all set to sparkle across all industries and from professional to personal lives. The future will be of Truly Autonomous Agents, Multi-modal Experiences, Personalized and Context-Aware AI, Enhanced Learning and Adaptability, and more.
Cross your fingers, something big we’ll witness with AI very soon.
Let’s head up to the next section!
How Does AI Work?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has moved from fictional stories to become a fundamental element of our everyday experiences. AI technologies, such as voice assistants like Siri and Alexa and content recommendation systems on streaming platforms like Netflix, Peacock TV, and Otters, are transforming digital interactions in our everyday lives.
The advanced functionality of these systems results from an intricate network of algorithms and computational processes that manage vast amounts of data. As AI use cases are increasing, for example, in healthcare, finance, government, manufacturing, etc., it is essential to understand how they work.
So, how does AI work?
The answer to this question has lots of twists and turns.
The simple answer is that AI functions by using computational systems to replicate some aspects of human intelligence.
But that we know already.
Present-day AI systems rely on machine learning techniques that allow algorithms to identify patterns from data instead of operating through predefined instructions. The initial step involves gathering extensive datasets that illustrate the problem the AI system needs to address. The collected data serves as the foundation for training mathematical models that can detect patterns and generate predictions.
For example, an image recognition AI system receives training by processing millions of labeled images. The system modifies internal parameters to reduce prediction errors throughout training.
AI system performance relies heavily on high-quality and substantial training data alongside advanced model architecture and sufficient computational resources.
Let’s break down the workings of AI in simple steps!
1. Input
Data is collected from various sources, including text, audio, and video. These are sorted into categories based on whether the algorithms can read them. A data processing protocol and criteria are then created.
2. Processing
Once the data is gathered and input, AI decides what to do with it. AI sorts and deciphers data using patterns it has learned until it recognizes similar patterns.
3. Outcomes
After processing, AI can predict outcomes in customer behavior and market trends. In this step, the AI decides whether a specific data set matches previous patterns. Decisions are made based on those outcomes.
4. Adjustments
In the event of a failure, AI learns from the experience and repeats the process under different conditions. Depending on the data set, the algorithm’s rules may need to be adjusted or slightly modified. Return to the outcomes step to align with the current data set.
5. Assessments
An AI’s final step is assessment. Using the data set, artificial intelligence synthesizes insights to make predictions. Afterwards, the algorithm can be adjusted based on feedback.
There is another secret waiting for you. Have you heard about the types of AI? No worries. Let’s move to the next section to learn more about it.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
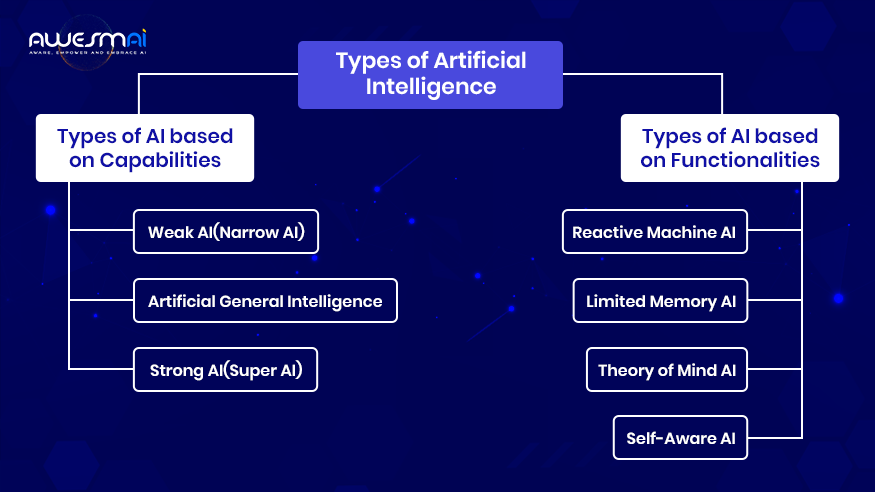
The AI types can be classified based on Capabilities and functionalities.
1. AI Capabilities
AI capability refers to how AI learns and can apply knowledge to solve complex problems requiring intelligence. Based on it, these can be categorized into the following.
a. Weak AI(Narrow AI)
Narrow AI refers to systems designed to execute a specific task with intelligence. Examples include voice assistants like Siri and Alexa, recommendation algorithms used by Netflix and YouTube, and email spam filters. These highly specialized systems cannot perform tasks outside their programmed domain or capabilities.
b. Artificial General Intelligence
AGI, aka Artificial General Intelligence, aims to create machines with thinking and learning capabilities that can apply intelligence like humans. It also refers to theoretical AI that aims to create systems that echo human intelligence, function as assistants to perform any task, and are adaptable and versatile. Some of its best examples are Generative AI products such as ChatGPT, Quantum Hardware, and Supercomputers.
c. Strong AI(Artificial Super Intelligence)
Superintelligence AI, or ASI, represents a future phase in the evolution of artificial intelligence, where machines achieve superior intelligence across all domains compared to humans. The potential development of this AI type remains theoretical, but it prompts important ethical and philosophical discussions about its societal implications. Hypothetically, it is predicted that one day it will rule over humans. Quite like a Sci-Fi movie, right?
2. AI Functionalities
This categorization narrows down types of AI based on their functionality in data processing, memory use, and learning capabilities.
a. Reactive Machine AI
Reactive Machine AI represents AI systems(with no memory) designed to do specific tasks. They process only available or given data and can’t store memory or recollect previous outcomes. Their use cases are only for basic autonomous functionalities like filtering spam and making recommendations to process historical data.
Examples: YouTube recommendations, IBM Deep Blue
b. Limited Memory AI
As the name implies, these AI systems function with limited memory capabilities. These systems can store past data and process it to predict outcomes. Simply put, limited memory AI systems work with a short knowledge base. The majority of AI applications are limited-memory AI.
These systems are powered by Deep Learning, which mimics the role of neurons found in the human brain. This enables a machine to gather insights from experiences and “learn” from them, enhancing the precision of its actions as time progresses.
Example: Virtual Assistants, Chatbots, self-driving cars
c. Theory of Mind AI
The concept of theory of mind in AI is the ability to understand and interpret the emotions of others, a concept that has been adapted from the field of psychology. Although it has not yet been accomplished, it is a significant milestone in the advancement of AI. Emotionally intelligent AI has the potential to revolutionize the technology industry; however, it also carries risks, such as job automation and potential errors.
d. Self-Aware AI
Similar to the Theory of Mind AI, Self-aware AI is also rigidly theoretical. If it were truly possible, it would be able to understand its own conditions and traits, as well as human feelings and thoughts. It would also feel, need, and believe things that are different from us.
So, hope you enjoyed reading this section. But, things about Artificial Intelligence don’t end here and there’s still a lot more to explore.
Artificial Intelligence Training Models
Training models for Artificial Intelligence (AI) function as critical components within machine learning. These models empower computers to detect patterns and solve complex problems, making data-driven decisions through extensive data analysis.
Each task and data type demands its own specific implementation of supervised learning techniques, together with unsupervised learning methods and reinforcement learning strategies.
Creating effective models requires both advanced algorithms and powerful computational resources. The evolution of AI models enables new applications across multiple areas, such as natural language processing and computer vision, alongside autonomous driving technology.
We can categorize AI learning models in the following:
1. Supervised Learning
The models that are trained on labeled data where the output is already known are called supervised learning models. Due to the capabilities of predictions using input-output pairs, supervised learning models have numerous use cases such as image classification, customer segmentation, fraud detection, and more.
2. Unsupervised Learning
Unlike supervised learning models, unsupervised learning models use unlabeled data. Without any detailed guidance, these models discover patterns and relationships. Its use cases include clustering (grouping similar data points), anomaly detection, recommendation systems, and image and video analysis.
3. Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning models learn through the environment, trial & error, receive rewards for actions, and get penalties for undesirable actions. Simply, these models can be described as learn through actions. Its real-use cases are algorithmic stock trading, self-driving cars, social media suggestions, and more.
Artificial Intelligence vs Machine Learning
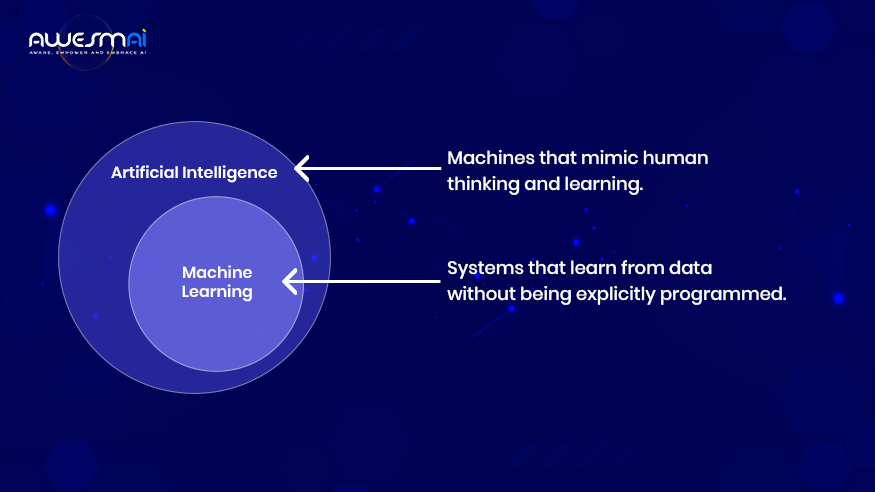
Machine learning(ML) is a subset of Artificial Intelligence, but both have some differences. On one side, AI mimics human intelligence, conversely, machine learning focuses on teaching a machine or system to execute a desired task and provide an expected outcome through identifying patterns.
Let’s examine AI vs. Machine Learning!
Artificial Intelligence (AI) – Artificial Intelligence involves creating machines that replicate human thinking and learning capabilities through programming.
Machine Learning (ML)– Machine Learning represents a specialized branch of AI that enables systems to learn from data without explicit programming instructions.
| Category | Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Machine Learning (ML) |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Artificial Intelligence represents a wide range of technologies | Machine Learning represents a specific area within AI |
| Goal | Artificial Intelligence strives to develop intelligent systems capable of performing human-like tasks | Machine Learning concentrates on teaching systems to learn through data analysis |
| Learning Approach | AI encompasses rule-based systems that operate without a learning process | ML necessarily includes learning patterns from data |
| Dependency | Artificial Intelligence operates through multiple methods, including rule-based systems | Machine Learning uses data extensively to enhance its capabilities |
| Decision-Making | Decision-making autonomy characterizes advanced AI systems | Machine learning models demand human assistance for their refinement |
| Applications | AI encompasses various applications from natural language processing to robotics | ML focuses mainly on prediction and classification tasks |
Apart from the difference between AI and Machine Learning, using both technologies is a powerful combination for mission-critical tasks. With the increasing amount of data and task complexity, AI and ML-powered systems help businesses with task automation, enhanced productivity, actionable insights, and data-driven decision-making. The common applications of AI & ML are in sectors such as healthcare, manufacturing, e-commerce, retail, financial services, telecommunications, and more.
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence
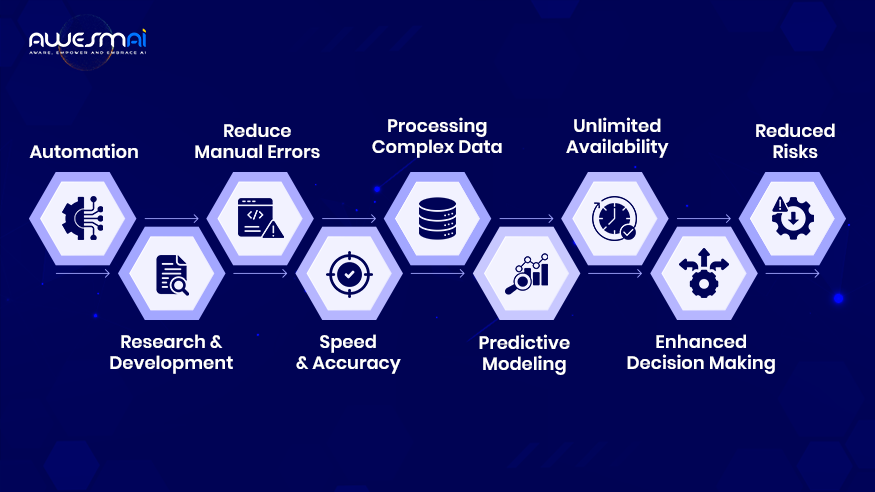
The benefits of AI are remarkable, not only for technology but for all industry domains. Here are some key benefits of Artificial Intelligence such as:
1. Automation
The most significant benefit of AI is the automation of repetitive tasks that consume time. These tasks can be anything like data collection, data entry, monitoring network traffic, manufacturing processes, and more. AI automation saves time, increases productivity, enhances creativity, and saves time.
2. Research and Development
The AI’s capability of analyzing a large amount of data helps in faster research and development. For example, predictive modelling, manuscript writing, idea generation, and even for disease detection.
3. Reduce Manual Errors
AI can get rid of mistakes made by humans while performing data processing, analytics, manufacturing assembly, and other tasks by using automation and applications that always do things the same way.
4. Speed and Accuracy
AI algorithms demonstrate superior speed and precision in processing massive data sets compared to human analysis, which results in faster pattern and trend identification.
5. Processing Complex Data
AI systems process complex multi-dimensional datasets to reveal insights that traditional methods fail to detect.
6. Predictive Modeling
AI develops predictive models that help anticipate future events, and these models prove helpful in disciplines such as epidemiology, finance, and environmental science.
7. Unlimited Availability
AI operates without the constraints of time, the necessity for breaks, or any other human limitations. In the cloud, AI and machine learning operate in an “always on” mode, constantly dealing with their designated tasks around the clock.
8. Enhanced Decision Making
AI empowers quicker and more precise predictions, facilitating reliable, data-driven decisions for decision support or fully automated processes. When coupled with automation, AI helps businesses to grab opportunities and handle crises as they arise, instantly and autonomously.
9. Reduced Risks
Some tasks require careful observation and are too risky for humans, such as handling large machinery and performing tasks in the worst weather conditions. Here, AI can help industries keep their workforce out of danger and injury risks.
Disadvantages of AI

The coin has two faces, so everything in this world and AI is no luxury. Often, we see the news or debates like, “What if AI becomes really intelligent as humans with emotions?” It seems hypothetical. Once upon a time, the moon landing was also the same; later, it happened.
Let’s look at some potential disadvantages of AI!
1. Job Displacement
As AI Automation is progressing through extensive research, one of the biggest fears is job displacement. Especially role-based tasks are especially vulnerable to it.
2. Privacy & Security
AI systems function based on large amounts of data, including sensitive data. Any breach can create chaos. Identity theft or misuse of data is the biggest concern for industries, especially banking and finance.
3. Lack of Emotional Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence lacks emotional intelligence, and right now, it can’t perform critical tasks that require human knowledge, years of experience, and emotions.
4. Environmental Concern
The high-power computing systems and infrastructure required to operate advanced AI systems consume significant power, which has the worst environmental effects.
Although scientists and researchers are also making efforts to use AI ethically, keep these AI disadvantages in mind.
10 Applications and Use Cases for Artificial Intelligence
Right now, AI has simplified numerous tasks requiring common human intelligence and utilizes the data, followed by training AI systems. From writing an email for leave to creating a product description for the next launch, AI can help you with everything.
We can classify AI applications based on the specific functions they perform, like:
1. Task Automation
Various domains use AI technology to automate repetitive tasks that require significant manual effort. Business operations benefit from robotic process automation (RPA), manufacturing uses automated assembly lines, and vehicles and drones operate autonomously through navigation systems.
2. Data Analysis and Insights
AI has great potential in performing data analysis and driving insights that can be impossible for humans to do quickly. Based on its capabilities, AI has great applications across areas like market research, demand forecasting, predicting consumer behavior, analyzing sales patterns, scientific discovery, and more.
3. Prediction & Forecasting
AI models can analyze historical data as a foundation to forecast future events and results. Business leaders use AI algorithms for sales forecasting, while maintenance teams rely on these models to predict equipment failures as part of predictive maintenance, alongside weather experts who use them for weather forecasting and risk managers who identify potential risks.
4. Natural Language Processing
Artificial Intelligence allows computers to process human language through understanding and interpretation and to produce output based on their language processing capabilities. NLP is the technology upon which systems such as chatbots and virtual assistants, language translation tools, sentiment analysis applications, and text summarization technologies rely.
5. Computer Vision
AI technology enables computers to process visual data from images and videos through interpretation. Computer vision’s use cases extend to facial recognition technology, object detection mechanisms, medical imaging analysis systems, and autonomous navigation solutions for vehicles and robots.
6. Personalized Experience
Businesses seek to personalize consumer experiences, and AI is a great tool for them. AI systems can use large language models (LLMs) to provide users and customers with customized experiences and targeted ads.
7. IT Operations Management
The correct term for AI-driven It operations management is AIOps(AI IT operations management). According to a research report, most IT enterprises are leveraging AIOps for root cause analysis, intelligent automation, threat detection, and more.
8. Decision Support
AI also simplifies how you can make crucial decisions for critical tasks. For example, in healthcare diagnostics or financial trading, AI analyzes complex events to produce insights and recommendations that assist humans in making better decisions.
9. Human-Computer Interaction
AI improves how humans interact with technology, voice recognition, gesture control, and intelligent agents that understand context.
10. Customer Support
Chatbots and voice assistants are examples of conversational AI systems that have gained popularity because they make technology more approachable, provide customer assistance, and lighten the workload for IT support staff.
10 AI Use Cases in Major Industries
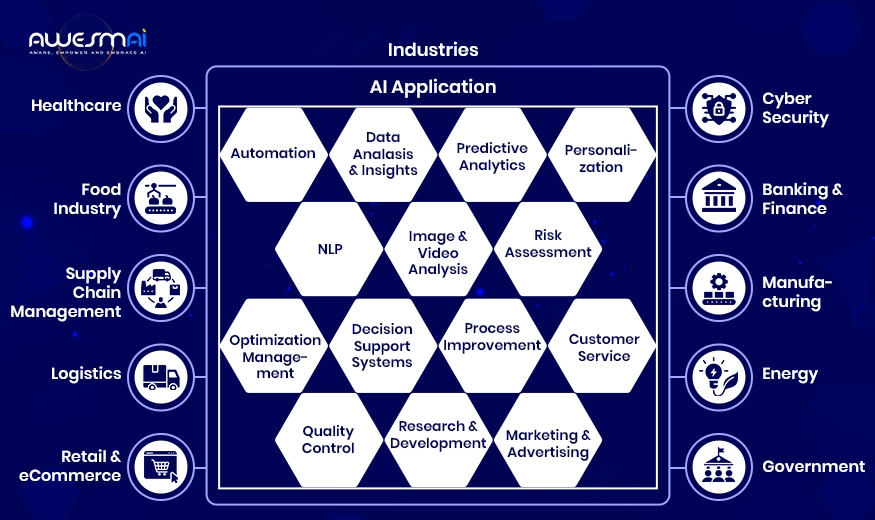
AI is a versatile technology. Due to its data-driven capabilities, it is applicable to almost all major industries. Here are some examples of AI applications across diverse industry sectors.
1. AI in Healthcare
Compared to conventional healthcare practices, AI in healthcare offers better and more personalized patient care. The healthcare industry is leveraging AI for data analysis, predictive analytics, diagnosis, medical imaging, remote patient care, and more.
Takeda, a Japan-based healthcare company, uses AI to research and develop new medicines. The company develops treatments and medicines for celiac disease, Parkinson’s disease, rare autoimmune disorders, and dengue.
2. AI in the Food Industry
Did you know that KFC uses AI? Yes, it’s true. KFC is now actively using AI in operations to improve customer experiences, including drive-thru ordering, call center assistance, analyzing traffic patterns, AI-driven marketing, and a super app for restaurant managers.
This is just one example; there are other, more real-life examples of AI in the food industry. Artificial intelligence helps in diverse ways, such as preventing food waste, food safety and quality assurance, supply chain automation, sustainability, and others.
3. AI in Supply Chain Management
Numerous reasons make AI a perfect choice for supply chain management such as outstanding customer experiences, reduced operational cost, automation, better efficiency, and more.
AI plays a crucial role in supply chain management, from demand analysis to warehouse management, from mitigating risks to compliance management, and more. Global supply chain companies such as Logiwa and VORTO are using AI for warehouse management to make their supply chain operations more efficient.
4. AI in Logistics
AI solves myriad challenges for the logistics industry, from operational cost reduction to enhanced delivery timelines. For example, top logistics firms like DHL, FedEx, or Maersk use AI in logistics for better route optimization for faster deliveries, demand prediction, supplier management, and more.
The benefits include reduced costs & expenses, demand accuracy, an impactful delivery timeline, and enhanced productivity.
5. AI in Retail & eCommerce
AI in retail and eCommerce offers a personalized product recommendations engine for online shoppers. The system maintains optimal inventory levels while managing supply chains. Dynamic pricing strategies utilize AI and customer sentiment analysis from reviews and social media content.
One of the best and simplest examples is online retailer Shien, which uses AI to customize product recommendations for its customers. In terms of use cases, from product discoveries to creating product descriptions and product images, AI is advantageous in several ways for the e-commerce industry.
6. AI in Cyber Security
Cyber threats are the biggest concern for industries worldwide, and conventional methods are useless. AI offers robust security through innovations. AI and Machine Learning improve security through threat detection automation, data analysis, and pattern identification.
Some top examples of brands using AI in cybersecurity are Google, IBM, Darktrace, and Crowdstrike.
7. AI in Banking & Finance
If you are looking for the top real-life examples of AI in banking and finance, it will be surprising that almost all global banking and financial organizations are using it nowadays. For example, JPMorgan for business loan automation, Bank of America introduced Erica – the virtual financial assistant for their customers.
AI in banking and finance is applicable for fraud prevention, anti-money laundering, personalized banking services, process automation, and advanced document processing.
8. AI in Manufacturing
It is interesting that predictive maintenance of factory machinery becomes possible through the application of AI. AI enhances production scheduling while simultaneously boosting energy efficiency. Another application is computer vision technologies, which conduct inspections to ensure product quality standards.
The top examples are BMW Group for high-quality auto parts manufacturing and GE for predictive maintenance and operational efficiency.
9. AI in Energy
Artificial Intelligence has taken utility power grids to new levels of intelligence and efficiency through real-time load and supply matching while enhancing grid resilience by predicting breakdowns and deploying repair teams, together with monitoring environmental risks and enabling predictive maintenance.
This is just one use case: AI in the energy sector is applicable to the oil & gas industry also. In terms of real-life examples, BP uses AI for smart drilling processes, Saudi Aramco utilizes AI tools for production activities, and Ørsted- a leading wind energy company, uses artificial intelligence to optimize wind turbine performance.
10. AI in Government
The benefits of AI are unlimited and has also encouraged governments and public sector agencies to leverage AI similar to the other sectors. The technology has applications in traffic management, urban planning, citizen services, public safety, and others.
Just as examples- the US Department of Energy introduced TranSEC analyzed traffic flow, Dubai’s AI assistant “RAMMAS,”
What is Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)?
Before we proceed further to read more about AI, you need to know what AGI is.
AGI systems exhibit some traits that distinguish it from other forms of AI like:
- Generalization Ability: AGI is adaptable and can transfer skills and knowledge achieved in one domain to another.
- Common Sense Knowledge: AGI can reason and make decisions based on a common understanding of facts, relationships, and social norms, possessing a vast knowledge repository.
Thus, as per the definition:
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) represents a theoretical AI model named “Strong AI” that functions as “human-level AI,” where an artificial system displays cognitive abilities equivalent to humans. The AI landscape is dominated by Artificial Narrow Intelligence systems, which execute specialized tasks with exceptional ability, compared to AGI systems, which could learn across multiple domains and adapt to versatile tasks like humans.
In terms of benefits, Artificial General Intelligence offers a lot, such as:
1. Unlimited Automation
In addition to repetitive tasks, AGI can automate entire sequences of cognitive activities, from strategy development to product design. AGI represents a complete transformation in value production.
2. Enhanced Decision-Making
AGI provides sophisticated responses to complex scenarios and identifies potential risks in real-time. By absorbing multiple sources of information, enterprise-wide machine learning emulates the superior decision-making skills of top executives.
3. Accelerated Innovation
AGI products provide innovative solutions that surpass traditional team capabilities by analyzing market trends and customer feedback. R&D, marketing, finance, and strategy departments can benefit from “intelligence.”
4. Personalized Customer Experiences
Dynamic adaptation across customer engagement fronts, from marketing to post-purchase service, facilitates new relationships and generates revenue.
What is Deep Learning?
Deep learning represents one of the most groundbreaking advancements in artificial intelligence. However, it often leaves business leaders wondering, “What is deep learning, and why is it important for my organization?”
It represents a specific specialization within machine learning, which in turn functions as a division under artificial intelligence. Traditional machine learning requires structured data and manual feature selection, whereas deep learning operates by employing brain-inspired algorithms to replicate human learning processes. Artificial neural networks consist of layered structures that algorithms create. The network layers in deep learning models develop the capability to identify increasingly sophisticated features directly from raw input data.
If you’re wondering what the use cases of Deep Learning are? Therefore, it includes- Application Modernization, Computer Vision, Customer Care, Digital Labor, Generative AI, Speech Recognition, and Natural Language Processing.
Differences Among AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning
We have collected more information about AI, its types, benefits, use cases, and more. To understand the concepts clearly, let’s differentiate between AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning.
| Aspect | Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Machine Learning (ML) | Deep Learning (DL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Build intelligent agents to solve tasks. | Enable machines to learn from data. | Teach machines to learn from data using neural networks. |
| Approach | Use various techniques to solve problems. | Use algorithms learned from data to improve performance. | Use multi-layered neural networks to process data. |
| Data Needs | Varies; can use knowledge representation or search. | Needs significant data learning patterns. | Needs very large amounts of data to train effectively. |
| Feature Engineering | Requires manual feature engineering. | Often requires manual feature engineering. | Automatically learns features from raw data. |
| Relationship | Broad concept; goal: create intelligent systems. | Subset of AI; focuses on learning from data. | Subset of ML; uses specific network architecture. |
| Evolution | Field started early AI research. | Grew from AI; developed algorithms. | Evolved from ML; utilizes deeper networks. |
Definition of Generative AI
Following our prior discussions about AI and its subfields, Machine Learning and Deep Learning, we now explore Generative AI, which stands as one of the most transformative advancements in technological progress. Our previous analysis separated these core principles, but to grasp Generative AI, we need to examine how these technologies merge to produce capabilities that appear magical.
Traditional AI focuses on analyzing and categorizing data but Generative AI creates original content such as text, images, music, code, and videos. GANs(Generative Adversarial Networks) and VAEs( Variational Autoencoders) alongside large language models(LLMs) use deep learning techniques and neural networks trained on extensive datasets to discover patterns that help them create original content. These models can create outputs that resemble human work through their machine creativity by utilizing user input and historical training data.
How does Generative AI work?
Generative AI analyzes training data patterns to create original content, including text, images, music, and code. It functions similarly to an artist who examines numerous paintings to learn diverse styles, techniques, and subject matters.
The following explanation shows the process of how generative AI works in a basic way:
1. Training
AI models acquire training through exposure to large collections of existing materials, including millions of sentences, images, and songs. During training, the model examines this data to recognize its fundamental structures and the patterns and relationships within it. The model learns to identify patterns of color combinations and shape configurations from images and music.
2. Learning Patterns
The AI doesn’t just memorize the data. The complex internal representation holds the fundamental aspects of the data distribution. The system acquires knowledge of rules and styles through content analysis. The model learns grammar, syntax, and facts in text but also gains knowledge about objects and composition in images.
3. Generating New Content
Once the model completes its training process, a user can provide it with a prompt. The AI produces content corresponding to the prompt while drawing similarity from its training data but remains distinct. It predicts the next word in a sentence and also predicts pixels in images or notes in melodies based on learned patterns and provided context.
Generative AI models depend on various architectures to perform their tasks. Transformer models excel at text generation, while Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are commonly used to produce images. However, the core idea remains the same: The essential process involves training models with available data to create fresh content that resembles original material.
Weak AI vs. Strong AI
Differentiating between Weak AI and Strong AI can be a hot topic for debate. As AI progresses at a skyrocketing speed, it might be difficult to differentiate between natural intelligence and Artificial Intelligence that learns on its own and is adaptable to anything.
While it will take time for AI to become super intelligent (Strong AI), what we are witnessing now is Weak AI.
Before we differentiate between them, let’s go through the definition part.
Strong AI
Strong AI is also known as Artificial General Intelligence, or AGI. Based on the theoretical concept, AGI or Strong AI has the capabilities or perform actions as humans do with their natural intelligence.
An AGI AI can understand and learn to apply its intelligence towards solving diverse problems, similar to how humans operate. The system is considered to have general abilities for reasoning and problem-solving in addition to perception and learning skills that apply to multiple tasks. Strong AI does not yet exist, but continues to drive active research and development efforts within the artificial intelligence domain.
Weak AI
The Weak AI refers to the Artificial Narrow Intelligence that is designed to perform specific tasks based on provided input. It doesn’t have its own abilities to think and learn. This AI replies to immediate requests and tasks, but does not store memory. The best examples of weak AI are voice assistants, image recognition software, chatbots, and others.
| Aspect | Weak AI (Artificial Narrow Intelligence) | Strong AI (Artificial General Intelligence) |
|---|---|---|
| Capability | Performs specific, narrow tasks. | Performs any intellectual task a human can. |
| Intelligence | Exhibits intelligence only within its function. | Possesses general cognitive abilities like humans. |
| Consciousness | Does not possess consciousness or self-awareness. | Theorized to possess consciousness (definition varies). |
| Current Status | Exists and is widely deployed. | Is currently theoretical; does not exist. |
| Learning | Learn within a limited domain from specific data. | Theorized to learn and apply knowledge broadly. |
| Examples | Voice assistants, image recognition, and recommendation systems. | None currently exist (hypothetical future systems). |
Augmented Intelligence vs. Artificial Intelligence
You have read some exciting information about AI while reaching this section, and now you have enough information. Do you know that another type of AI also exists, apart from the types we have seen in this blog earlier?
Have you heard about Augmented AI?
Augmented AI refers to Artificial Intelligence that enhances human abilities to perform tasks, analyze data, and make better decisions. It enables AI to serve as either a tool or a partner while processing data and automating repetitive tasks so humans can direct their efforts toward superior cognitive abilities, including critical thinking and innovative problem-solving. The system maintains human involvement while maximizing combined human-machine intelligence benefits through collaborative efforts.
Therefore, here it is AI vs Augmented AI to understand the concept in a better way.
| Aspect | Augmented Intelligence | Artificial Intelligence |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Enhance human capabilities and decision-making. | Create intelligent systems to perform tasks. |
| Role of Human | Human intelligence is required, and AI assists and supports. | AI can operate autonomously; it may replace humans. |
| Relationship | Human-computer partnership; collaborative. | Machine intelligence can be independent. |
| Focus | Improve human performance with AI tools. | Develop machines that mimic human intelligence. |
| Outcome | Enhance human potential; better human decisions. | Automates tasks; can lead to autonomous systems. |
| Examples | AI suggesting diagnoses to doctors, AI giving insights to financial analysts, and smart assistants providing information. | Systems flagging fraudulent transactions automatically, recommendation engines suggesting content, and autonomous vehicles navigating. |
Ethical Use of Artificial Intelligence
The ethical use of AI ensures that AI is deployed in a way that doesn’t harm humans and aligns with human values and principles.
The key ethical considerations include:
- Bias and Fairness: AI learns from data. So, when making an AI system learn, ensure that the data is not biased toward race, gender, age, or ethnicity.
- Privacy: An AI and ML-powered system often uses vast amounts of data that might include sensitive information, so there must be a secure protocol to keep data safe from any cyber threat.
- Transparency: An AI system must be understandable and interpretable. Simply, users must easily understand how and why it produces a specific output.
- Accountability: If AI causes harm, then it must be clear who is responsible for it. This will help implement AI ethically.
- Human Control: While AI systems work autonomously, ethical considerations dictate that humans must control them.
- Job Displacement: Displaced jobs are one of the biggest concerns. If any organization applies AI to its operations and business practices, there must be reskilling and upskilling initiatives to prevent job displacement.
The fundamental principle of ethical AI usage demands that AI development and deployment support humanity’s welfare and create beneficial societal impacts while honoring essential human rights and values.
Conclusion
The progress of AI across diverse fields is tremendous, and nearly all industries are adopting AI as a core strategy. It has solved numerous challenges and is helping businesses improve productivity through automation. Technologies like Deep Learning, Machine Learning, Artificial Neural Networks, and Natural Language Processing are reshaping the world.
Although AI currently has only the capabilities to process input and produce output based on limited learning, the future will be beyond our expectations. Apart from autonomy, AI also offers benefits to improve human capabilities, such as analysis and better decision-making, but its ethical use is also important.
So, concluding this blog, it is true that AI is everywhere, but how you use it depends on the requirements. In terms of business applications, AI is the technology you can consider to improve your business practices and long-term growth. Remember, using it ethically can make this world more beautiful.